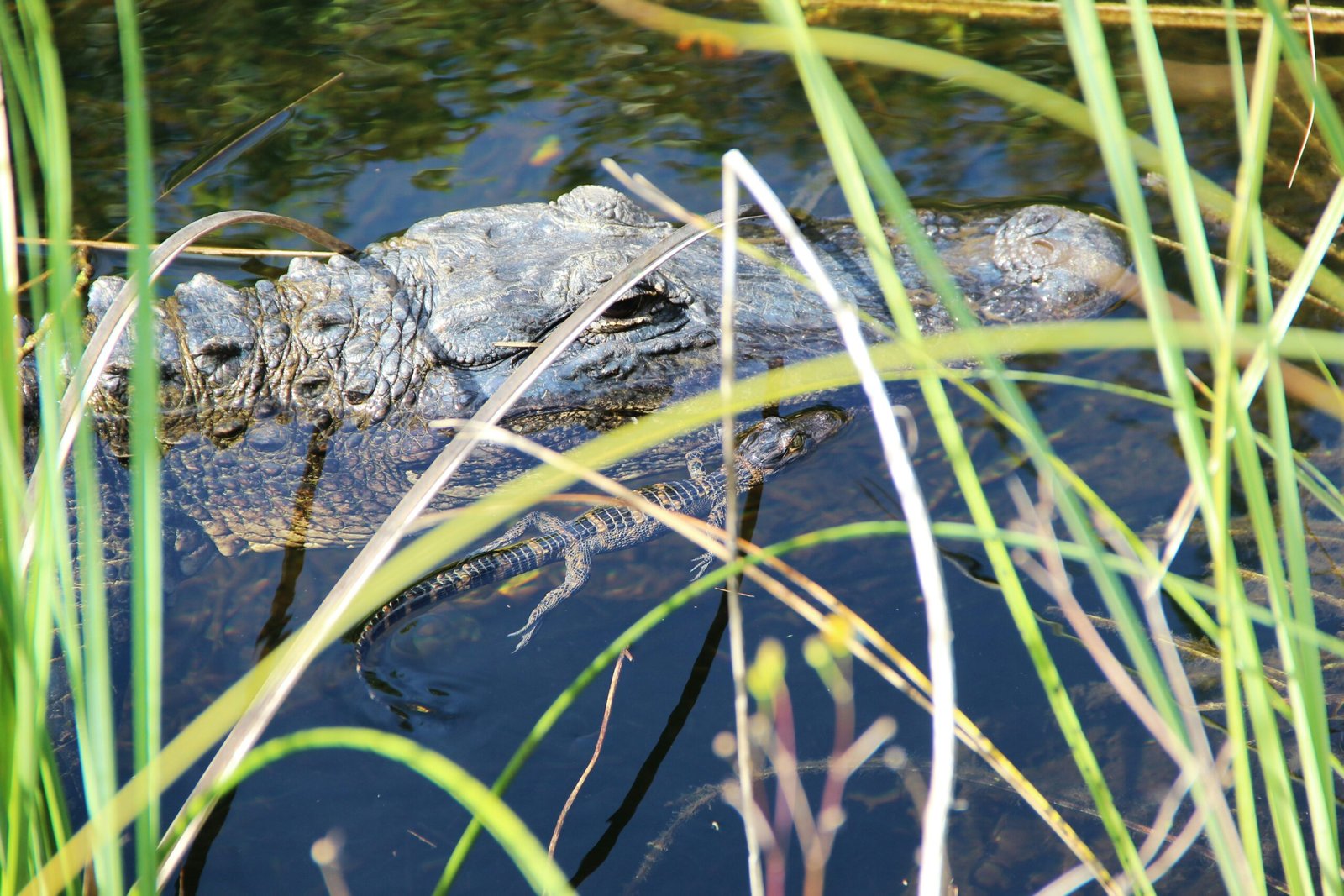
Understanding the Legal Requirements for Alligator Leather Trade
Imagine you stumble upon a luxurious alligator leather handbag and can’t help but marvel at its exquisite craftsmanship. But have you ever wondered about the legalities surrounding the alligator leather trade? In this article, we will explore the legal requirements that govern this industry, ensuring that every piece of alligator leather you come across is ethically sourced and compliant with regulations. From permits to conservation efforts, we will shed light on the intricate world of alligator leather trade.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
International Legal Framework
CITES and alligator species
The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) plays a crucial role in regulating the trade of alligator species. CITES is an international agreement between governments aiming to ensure that international trade of wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival. Alligator species are listed under CITES, which means that their trade is subject to specific regulations and controls.
Appendix I, II, and III
CITES categorizes species into three appendices based on their conservation status and the level of protection required. All species of alligators are listed in either Appendix I, II, or III. Appendix I includes species that are most threatened with extinction and hence provides them with the highest level of protection. Appendix II includes species that are not necessarily threatened with extinction yet, but their trade must be regulated to ensure their survival. Appendix III includes species that are protected within at least one country which has asked for cooperation from other CITES member countries to control their trade.
Role of CITES in regulating alligator trade
CITES regulates the trade of alligator species through a permit system. Before engaging in any trade involving alligator products, individuals and businesses must obtain the necessary permits from the appropriate CITES authorities in their country. These permits ensure that the trade is legal and sustainable. CITES also encourages international cooperation among member countries to prevent illegal trade and protect alligator species from overexploitation.
Regional and National Regulations
Role of regional agreements
In addition to international regulations, regional agreements play a significant role in the regulation of alligator trade. Regional agreements, such as those within the European Union or between countries in a specific geographic area, can have their own regulations that further restrict or control alligator trade. These agreements allow for a collaborative approach in ensuring the protection of alligator species within a specific region.
Country-specific legislation
Each country may have its own legislation regarding the trade of alligator species. These country-specific laws provide additional protection and regulation to safeguard alligator populations. These laws may establish stricter requirements for permits, impose limitations on trade, or set specific conservation measures.
Permit requirements
Regardless of international or regional regulations, individual countries may require specific permits for the trade of alligator products. These permits ensure that the trade is conducted legally and in compliance with national conservation and wildlife protection laws. It is of utmost importance for individuals and businesses involved in alligator trade to familiarize themselves with the permit requirements in their respective countries to avoid any legal complications.
Protected Species
Identification of protected alligator species
To comply with the legal regulations surrounding alligator trade, it is essential to accurately identify protected alligator species. These species may have specific physical characteristics or markings that distinguish them from other non-protected species. It is crucial to have a thorough understanding of the unique traits and identification methods for the different species to avoid any unintentional non-compliance.
Endangered and threatened status
Alligator species may have different conservation statuses, ranging from endangered to vulnerable or threatened. Understanding the specific status of each species is crucial in determining the level of protection and regulation required for their trade. This information helps in implementing appropriate measures to safeguard their populations effectively.
Restrictions on trade and products
Protected alligator species generally face restrictions on their trade and the products derived from them. These restrictions may include limitations on the number of individuals that can be harvested, quotas on the number of products that can be traded, or complete bans on specific products. It is essential for individuals and businesses involved in alligator trade to adhere to these restrictions to ensure the sustainable and legal sourcing of alligator products.
Sustainable Sourcing
Harvest quotas and monitoring
To ensure the sustainability of alligator populations, harvest quotas are often established. These quotas determine the maximum number of alligators that can be harvested each year, taking into account the species’ reproductive rates and overall population health. Strict monitoring mechanisms are put in place to track the number of alligators harvested and ensure compliance with these quotas. This monitoring enables authorities to make informed decisions regarding the sustainable sourcing of alligator products.
Traceability requirements
Traceability is crucial in the alligator leather trade to guarantee legal sourcing and prevent illegal practices such as poaching and smuggling. Authorities require strict traceability measures to track the journey of alligator products from their origin to the final consumer. This traceability aids in identifying and eliminating any potential illegal or unsustainable practices along the supply chain.
Certification programs
Certification programs, such as the Audubon Cooperative Sanctuary Program and the Sustainable Agriculture Network, play a vital role in promoting sustainable sourcing of alligator products. These programs provide guidelines and standards for sustainable practices, and businesses that adhere to these standards can obtain certifications. Certifications serve as proof of sustainable sourcing and can help consumers make informed purchasing decisions.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Anti-illegal Wildlife Trade Measures
Enforcement agencies and initiatives
Enforcement agencies dedicated to combatting illegal wildlife trade play a crucial role in regulating the alligator trade. These agencies work to enforce national and international regulations, conduct inspections, and investigate cases of illegal activities. Initiatives like Interpol’s Wildlife Crime Working Group and the International Consortium on Combating Wildlife Crime contribute to international cooperation in tackling the illegal wildlife trade, including efforts related to alligator species.
Combatting illegal poaching and smuggling
Illegal poaching and smuggling pose significant challenges to the conservation of alligator species. Governments and organizations employ various strategies to combat these illegal activities. These strategies may include increasing surveillance and patrol efforts in vulnerable areas, implementing stringent penalties for offenders, and raising public awareness about the consequences of illegal wildlife trade.
Challenges and advancements
Despite efforts to combat illegal wildlife trade, various challenges persist. Organized criminal networks, corruption, and the vast nature of the illegal trade make enforcement challenging. However, advancements in technology, such as the use of DNA analysis to identify the origin of alligator products, and international collaborations continue to enhance the capacity to detect and deter illegal activities.
Environmental Impact
Sustainability concerns
The alligator leather trade has environmental implications that must be carefully addressed. Unsustainable sourcing practices can lead to the depletion of alligator populations and disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems. Authorities and stakeholders must prioritize sustainable management to ensure the long-term survival of alligator species and minimize the ecological impact.
Ecological effects of alligator removal
Alligator removal, particularly when not conducted sustainably, can have a cascading effect on ecosystems. Alligators play a vital role in their habitats as top predators, influencing the populations of other species and maintaining the ecological balance. Overexploitation can disrupt these ecosystems, affecting biodiversity and potentially causing negative consequences for other species.
Conservation programs and efforts
Conservation programs and efforts play a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of the alligator leather trade. These programs focus on habitat conservation, captive breeding programs, and research to understand alligator populations better. By implementing conservation measures and promoting sustainable practices, stakeholders contribute to the preservation of alligator habitats and the overall ecological well-being of their ecosystems.

This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Welfare and Ethical Considerations
Animal welfare standards
Responsible and ethical sourcing of alligator products encompasses animal welfare considerations. Ethical standards include ensuring proper care and treatment of captive alligators, providing adequate space and quality of life, and minimizing stress or harm during farming and harvesting. Adhering to these standards ensures that the welfare of alligators is prioritized throughout the entire production process.
Ethical sourcing and farming practices
Ethical sourcing extends beyond animal welfare to encompass sustainable farming practices. Farms that engage in alligator breeding should operate in a manner that minimizes their environmental impact, maintains genetic diversity, and contributes to the conservation of alligator species. Ethical sourcing practices ensure that alligator products come from responsibly managed farms committed to sustainability.
Alternative materials and vegan options
For individuals who seek to avoid animal-derived products altogether, alternative materials and vegan options provide ethical and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional alligator leather. Innovative materials, such as plant-based and synthetic leathers, offer a cruelty-free option without compromising on style or quality. These alternatives provide options for individuals to align their values with their purchasing choices.
Supply Chain Transparency
Transparency in sourcing and processing
Supply chain transparency is essential to ensure that alligator products originate from legal and sustainable sources. Transparency should include comprehensive documentation and records of the origin and processing of alligator skins. By having a transparent supply chain, businesses and consumers alike can make informed decisions and support ethical and sustainable practices.
Certification of origin
One way to establish transparency in the alligator leather trade is through the certification of origin. Certificates of origin provide documented evidence that alligator products were sourced from legal and sustainable farms and underwent the required regulatory processes. These certificates not only demonstrate compliance with legal requirements but also increase consumer trust and confidence.
Consumer awareness and education
Promoting consumer awareness and education is crucial to achieving a transparent and sustainable alligator leather trade. By raising awareness about the importance of responsible sourcing, consumers can make informed choices and support businesses that prioritize ethical and sustainable practices. Education initiatives can help dispel misconceptions and provide comprehensive information about the alligator leather industry.
Trade and Export Controls
Import/export permits
Trade and export controls on alligator products involve obtaining the necessary import and export permits. These permits ensure that all trade complies with national and international regulations. Businesses engaged in the import and export of alligator products must obtain the appropriate permits to demonstrate compliance with legal requirements and demonstrate responsible trade practices.
Restricted and prohibited trade
Certain countries or regions may have specific restrictions or prohibitions on the trade of alligator products. These restrictions may include limitations on importing or exporting certain alligator species or their products. It is important for businesses to familiarize themselves with these restrictions to avoid engaging in illegal activities inadvertently and to maintain compliance with trade regulations.
Customs and border controls
Customs and border controls play a crucial role in enforcing trade regulations related to alligator products. These controls ensure that all imports and exports of alligator items are accompanied by the necessary permits and comply with legal requirements. Customs agents and border officials play a vital role in preventing illegal trade, identifying counterfeit products, and ensuring compliance with trade regulations.
Penalties and Legal Consequences
Fines and penalties for illegal trade
Engaging in illegal alligator trade can result in severe fines and penalties. These consequences serve as deterrents and reinforce the importance of complying with legal requirements. The exact fines and penalties vary depending on the jurisdiction and the severity of the offense. It is essential for individuals and businesses involved in alligator trade to be aware of the potential consequences to avoid legal repercussions.
Legal repercussions for non-compliance
Non-compliance with legal regulations can lead to legal repercussions, including criminal charges and prosecution. Authorities actively monitor the alligator leather trade to identify any instances of non-compliance. By adhering to the legal requirements and implementing responsible practices, businesses can avoid legal complications and maintain their reputation in the industry.
Case studies and notable prosecutions
Case studies and notable prosecutions related to illegal alligator trade highlight the significance of compliance and the seriousness of illegal activities. Examples of successful prosecutions serve as reminders that the illegal trade in alligator products is a priority for law enforcement agencies. By studying these cases, individuals and businesses can gain insights into the consequences of non-compliance and the importance of adhering to legal regulations.
In conclusion, the legal requirements surrounding alligator leather trade involve a comprehensive framework of international and regional regulations, protected species considerations, sustainable sourcing practices, anti-illegal trade measures, environmental impact awareness, welfare and ethical considerations, supply chain transparency, trade controls, and penalties for non-compliance. Understanding and adhering to these requirements are crucial for ensuring the legal and sustainable sourcing of alligator products and contributing to the conservation of alligator species and their habitats.



